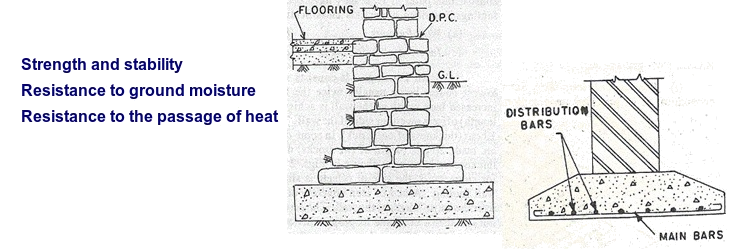
Foundation
The foundations of buildings bear on and transmit loads to the ground. The foundation is that part of walls, piers and columns which is in direct contact with and transmit loads to the ground.
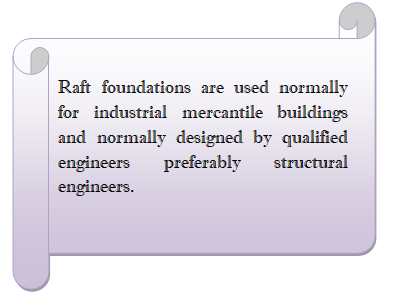
The foundations of varying types depending upon load requirement, ground conditions and prevailing practices in the region. A strip foundation is a continuous strip of concrete under walls, an isolated footing is a concrete isolated base under piers and columns, a raft foundation is a continuous base under the whole of the building and a pile is a concrete column or pillar cast in or driven into the ground to support a concrete base or ground beam.
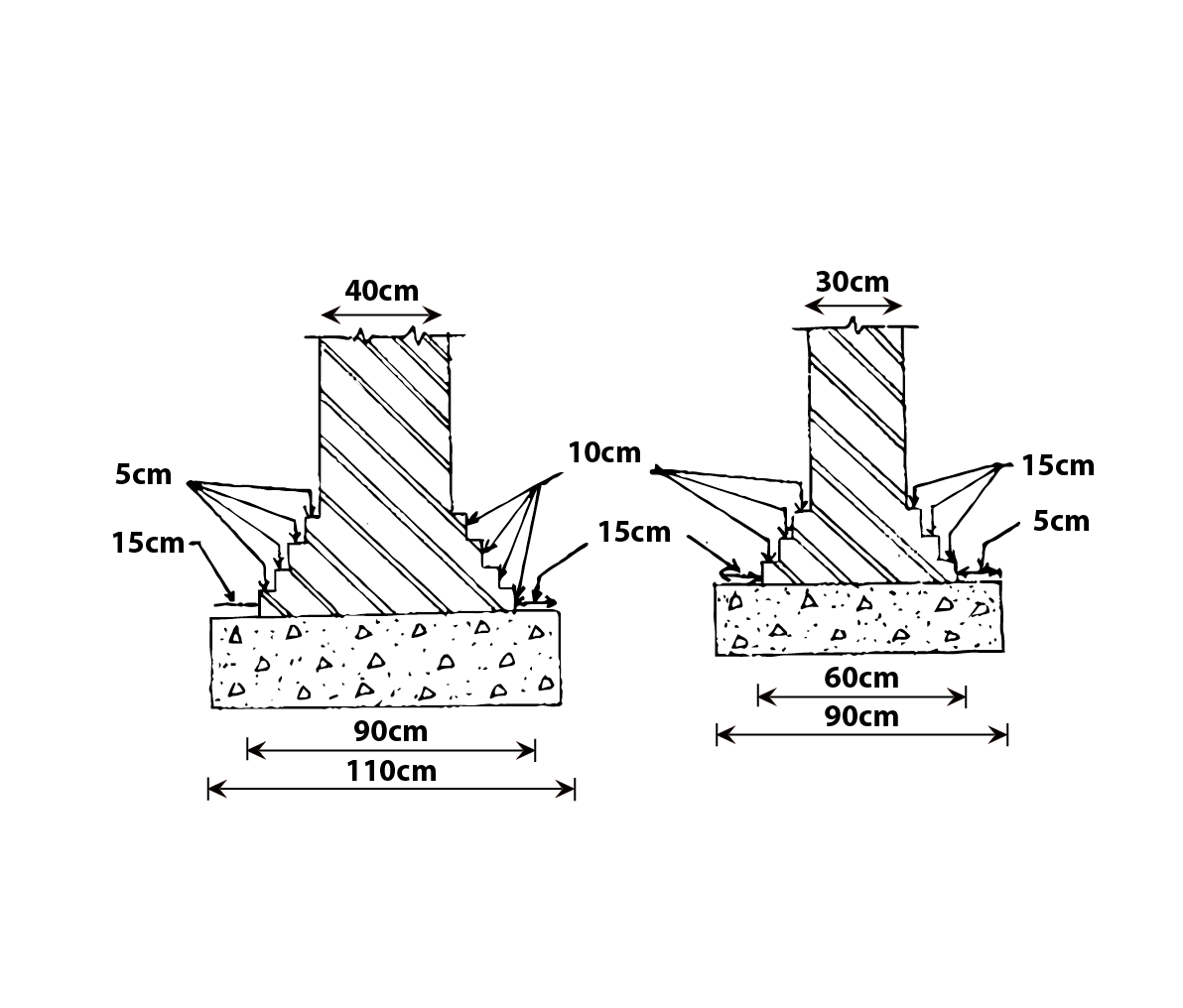
Stone wall footing/Reinforced Concrete Footing
The Functional Requirements of foundation in general :